What Is Retail Packaging?
2025-09-13 11:45:35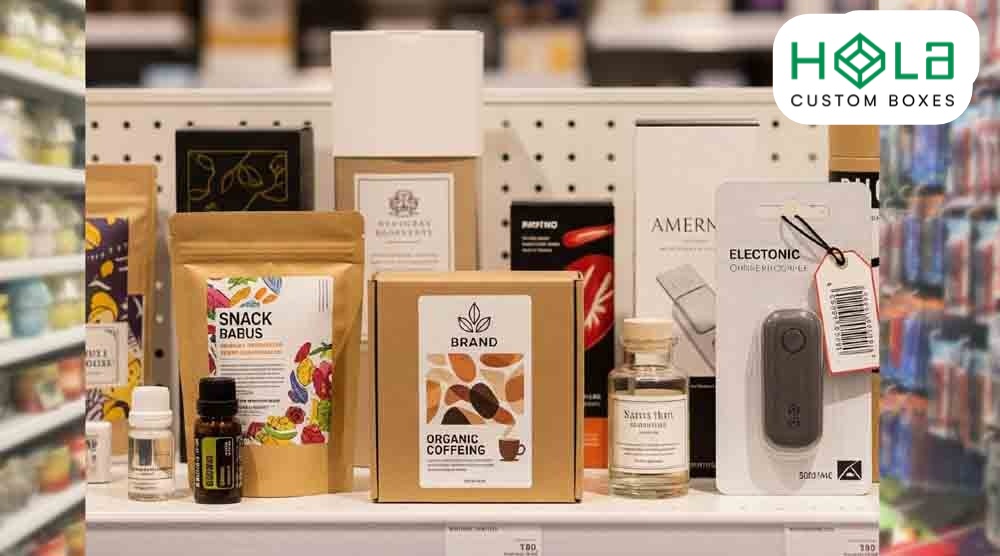
What Is Retail Packaging?
Retail packaging is the engineered interface between your product and the shopper—materials, structures, and graphics that protect, meet regulations, and drive purchase. You’ll specify dielines, board grades, inks, and coatings to balance protection with shelf impact and clear information. Unlike ship-only boxes, it prioritizes display, unboxing, and brand standards while hitting sustainability targets (recycled content, recyclability, material health). Choose paperboard, rigid boxes, or barrier bags to match risk and shelf life. Next, see formats, examples, and design tips.
Main Points
- Retail packaging is the engineered system of materials, structures, and graphics that protects products and drives purchase decisions in retail environments.
- It balances product protection, regulatory compliance, and visually appealing information that informs and persuades shoppers.
- Unlike non-retail packaging, it emphasizes shelf impact, branding, and premium unboxing experiences alongside functionality.
- Common formats include paperboard cartons, rigid boxes, and sealed bags, with options for eco-friendly fibers and premium printing.
- Effective retail packaging increases brand visibility, communicates value, and can significantly improve sell-through rates.
Definition and Purpose of Retail Packaging
Although it looks simple, retail packaging is a system of materials, structures, and graphics engineered to protect a product, comply with regulations, and drive purchase behavior at point of sale.
You define retail packaging as the engineered interface between product and consumer, where design, packaging materials, and labeling standards converge. Its purpose is dual: safeguard contents through transit and present a visually appealing, information-rich surface that signals brand, marketing intent, and quality.
Core shelf cartons live under retail packaging boxes
You use dielines, board grades, inks, and coatings to optimize shelf impact, brand recognition, and customer experience. Clear claims, instructions, and serialization guide choice and elevate the unboxing experience.
Drawing on high-quality materials and durability testing, Hola Custom Boxes ensures products arrive safely while enabling custom printing for strong brand recognition.
Key Differences Between Retail and Non-Retail Packaging

While both aim to protect goods, retail and non-retail packaging diverge in intent, materials, and specification. You prioritize Retail packaging when the goal is to attract the customer’s eye, deliver product information, and drive branding and marketing. Non-retail packaging favors rugged, cost-effective packaging solutions optimized for transit and storage. Key differences include graphics, unboxing experience, and per-unit cost. Retail formats often use decorative substrates; non-retail opts for corrugated and cushioning.
Premium giftable SKUs use custom rigid gift packaging boxes
Businesses can leverage custom fold-and-assemble boxes for cost-efficient, versatile packaging that supports branding and protection needs across both contexts.
| Focus | Retail packaging | Non-retail packaging |
|---|---|---|
| Intent | Shelf impact, marketing | Protection, logistics |
| Materials | Decorative board, glass | Corrugated, bubble wrap |
| Experience/Cost | Premium unboxing; higher cost | Minimal design; cost-effective |
Consider product type, market, and budget.
Materials and Formats Commonly Used
Given those differences in intent, you choose materials and formats that balance shelf impact, protection, and cost within recognized packaging standards.
In retail packaging, you match materials to product risk, shelf life, and packaging design constraints. Paperboard boxes deliver lightweight, printable panels for custom retail packaging; specify recycled content and coatings compatible with sustainable packaging goals.
Match materials to product risk, shelf life, and design—lightweight, printable paperboard supports sustainable retail packaging goals.
Rigid boxes provide crush resistance for premium SKUs, with precise tolerances and protective inserts. Foil sealed bags create high-barrier structures against moisture, oxygen, and UV, ideal for perishables.
You may also select plastics, glass, or eco-friendly packaging using hemp or bamboo fibers to meet performance targets. For cosmetics and beauty items, consider premium printing options like offset with matte or gloss finishes, spot UV, and embossing to elevate shelf appeal while maintaining sustainability with recyclable cardboard or kraft substrates.
Benefits for Branding and Sales
Because retail packaging functions as both protection and promotion, it directly drives brand visibility, preference, and conversion.
Use custom packaging as a calibrated marketing tool: it protects products, communicates product information with accuracy, and elevates perceived value through aesthetically pleasing packaging.
Precision packaging design differentiates on crowded shelves, creating a memorable unboxing experience that boosts consumer loyalty and repeat purchase—52% return when packaging appeals.
Clear labeling, compliant typography, and durable substrates reduce damage rates and increase trust.
In a market approaching $4 trillion, optimized retail packaging improves sell-through by uniting structural integrity, print fidelity, and brand visibility into a measurable sales engine.
For point-of-sale uplift, deploy custom display packaging boxes
Sustainability Considerations and Eco-Friendly Options

Even as aesthetics and protection remain core, you should specify retail packaging with measurable sustainability criteria that meet standards and reduce lifecycle impact.
Define targets for recycled content, recyclability, and material health to align with consumer values and strengthen brand reputation. Select packaging options that use recyclable materials—paper, cardboard, metals—and vetted biodegradable plastics where infrastructure exists.
Set targets for recycled content, recyclability, and material health; choose recyclable or vetted biodegradable materials where infrastructure exists.
Design for a circular economy with mono-materials, minimal inks, and efficient dimensions; you’ll often cut costs as eco-friendly packaging scales.
- Validate claims with certifications and LCA.
- Maximize fiber recovery rates.
- Prefer renewable, responsibly sourced inputs.
- Engineer disassembly and clear disposal labeling.
Types of Retail Packaging With Examples
Four common retail packaging types address distinct product and performance needs: custom packaging for brand-specific structures and graphics, flexible formats for lightweight barrier protection, rigid formats for impact resistance and display integrity, and eco-friendly options that prioritize recycled or biodegradable inputs.
You’ll use custom retail packaging to protect and present premium SKUs, enhance product visibility, and reinforce brand identity with precision die-cuts, coatings, and print.
Flexible retail packaging, including foil sealed bags, preserves freshness and reduces freight mass.
Rigid retail packaging secures electronics and glassware, sustaining shelf shape and an elevated unboxing experience.
Eco-friendly retail packaging leverages recycled fiber or bio-based films to attract customers.
Build a consistent shelf system with our retail packaging collection.
Tips for Designing Effective Retail Packaging

Having mapped common formats—custom, flexible, rigid, and eco-forward—you now need execution standards that convert a structure into shelf-ready performance.
To create packaging that earns brand loyalty, align design options with performance metrics and compliance.
Earn loyalty by aligning packaging design with performance metrics, compliance, and real-world durability.
- Specify substrates: choose durable boards, coextruded films, or molded fiber; verify drop, compression, and seal integrity so product packaging survives transit.
- Prioritize eco-friendly materials without compromising strength; document recyclability and certifications.
- Use engaging graphics, calibrated color, and tactile finishes; maintain barcode/UDI legibility and clear product information.
- Engineer the unboxing experience for customers: easy-open features, tamper evidence, and right-size components; guarantee packaging is designed for efficient kitting and replenishment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is the Meaning of Retail Packaging?
Retail packaging means the engineered system you use to enclose products for sale, balancing product protection, packaging materials, and packaging design with visual appeal and branding impact.
You optimize sustainable packaging to shape consumer perceptions, align with marketing strategies, and meet standards.
You evaluate cost considerations, durability, and eco friendly options while ensuring compliance and print legibility.
You select substrates, inks, and structures that safeguard goods, enhance shelf presence, and enable efficient distribution.
What Does Retail Packaging Mean on Amazon?
Retail packaging on Amazon means the branded exterior your Amazon product ships in, optimized for retail branding, consumer perception, and product protection.
You’ll select packaging types and packaging design that fit shipping considerations, packaging regulations, and cost implications. You must meet Amazon’s standards for durability, labeling, and barcodes.
Prioritize eco friendly packaging where possible, balancing materials, cushioning, and size to minimize damage, reduce dimensional weight, and deliver a professional, compliant unboxing experience.
What Does "No Retail Packaging" Mean?
“No retail packaging” means you receive the item with no packaging beyond essentials for product protection and shipping considerations.
You bypass decorative packaging types and extra packaging materials. You’ll see lower brand visibility and fewer marketing strategies, but clearer cost implications.
Many consumer preferences favor reduced environmental impact and waste. Expect bulk or plain cartons, minimal labeling, and possibly missing accessories typical of retail sets.
Verify compatibility, warranty handling, and any handling standards before purchase.
What Is the Difference Between Bulk Packaging and Retail Packaging?
Bulk vs retail differs in purpose and execution: you optimize product protection and distribution channels with minimal packaging materials, while retailers prioritize shelf appeal, branding strategies, and consumer psychology.
You’ll see a cost comparison favor bulk, as retail adds graphics, inserts, and hang tabs. You mitigate environmental impact using recyclable boards; retail often increases material use.
Bulk drives logistics efficiency; retail boosts sales performance through labeling standards, barcodes, and tamper-evidence that support merchandising and compliance.
(Recommended Products)
